We use cookies to improve the services we offer you. By continuing to browse this site, you consent to keep them in accordance with our Privacy Policy.
×We use cookies to improve the services we offer you. By continuing to browse this site, you consent to keep them in accordance with our Privacy Policy.
× 8,222
8,222
 6 min
6 min
When you’re just starting out in video editing, it’s easy to get lost in all that specific terminology. It can be particularly annoying when you’re trying to watch some online editing tutorials and you realize that you don’t understand a word. To save you the hassle of googling each collocation all the way, we’ve compiled this essential vocabulary checklist: this set of flashcards should be enough to familiarize you with most of the terms you need.
Video Editing Terminology Flashcards
Chromakey
Method of electronically inserting an image from one video source into the image of another through areas designated as its “key color.” It is frequently used on news programs to display weather graphics behind talent.
Enjoy our special discount for all blog readers!
Promocode: SUPERBLOG
Download Movavi Video Editor Plus with 10% discount for Windows
Download Movavi Video Editor Plus with 10% discount for Mac
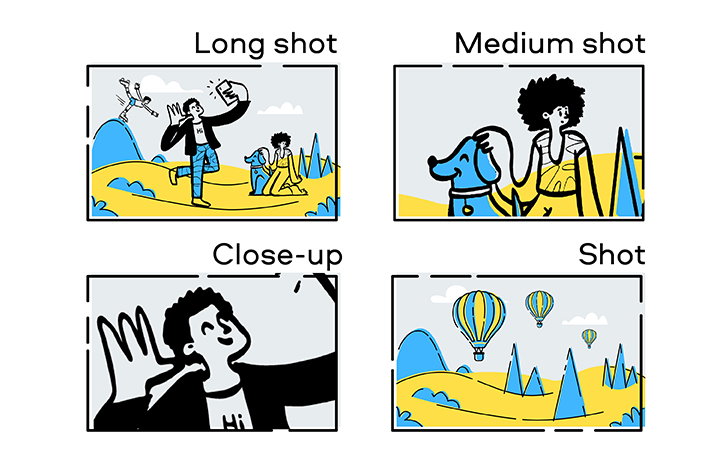
Close-up
A framing in which the scale of the object shown is relatively large; most commonly, a person’s head seen from the neck up, or an object of a comparable size that fills most of the screen.
Color Correction
A technical process that fixes color issues and makes footage appear as naturalistic as possible. The idea is for colors to look clean and real, as human eyes would see them in the real world.
Color Grade
The color grading process adds atmosphere and emotion to shots by coloring footage in new, often unnatural ways.
Continuity editing
The ‘Classical Hollywood’ style of editing; intended to establish a logical coherence of time and space between shots, suggesting that everything in the scene is physically continuous.
Cross cutting
Cut into action that is happening simultaneously. This technique is also called parallel editing. It can create tension or suspense and can form a connection between scenes.
Cutaway
A shot that interrupts a continuous action, “cutting away” to another image or action, often to abridge time.
Fade
A gradual change of volume used to change between clips of audio.

Frames
The individual video images that make up a moving sequence. Video formats and individual clips are typically described in terms of the resolution of the individual frames, and the frame rate at which they are played.
HDR (High Dynamic Range)
A photographic compilation that allows for the combination of luminance data from different exposure values.
Jump cut
An elliptical cut that appears to be an interruption of a single shot. Either the figures seem to change instantly against a constant background, or the background changes instantly while the figures remain constant.

Keyframe
A frame that signifies a change in the Timeline of a Flash movie, such as an object being animated.
Lip-synch
Proper synchronization of video to audio.
Long shot
A framing technique used to capture the environment and full body of subject.
Mask
A feature that lets you protect or modify a particular area; created using a marquee.
Medium shot
A relatively close shot, revealing the human figure from the knees or waist up.
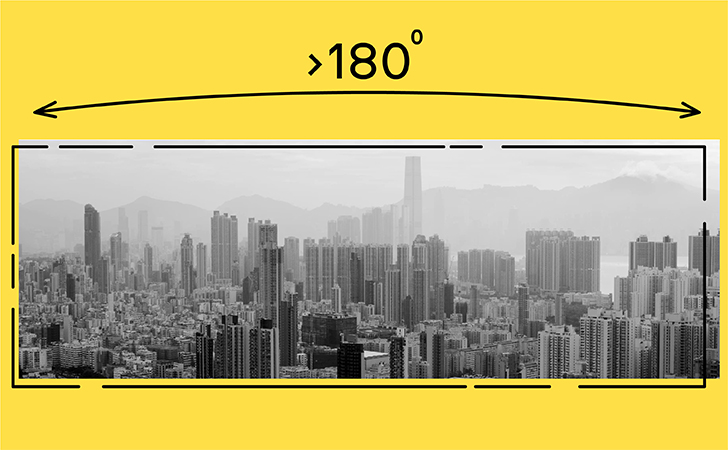
Panorama
A complete view of a surrounding area.
Post-Production
All phases of production following recording of video, i.e. capturing, editing, titling, exporting, etc.
Raw Footage
Pre-edited footage, usually direct from the camcorder.
Render
The process by which a computer processes information from a coded data source and uses that information to produce and display an image.
Ripple Edit
A type of trim which automatically moves edited clips forward or backward in the Timeline in relation to an inserted or deleted clip.
Rough cut
The crudely edited footage of a movie before the editor has tightened up the slackness between shots. A kind of rough draft.
Rule of Thirds
Divides the frame into 9 sections, points of interest should occur at 1/3 or 2/3.
Sequence
An edited assembly of audio and video clips.
Slide
A slide edit means moving a clip left or right in the timeline while simultaneously adjusting other clips to compensate.
Slip
A slip edit means adjusting the in and out points of a clip simultaneously by the same amount in the same direction. The duration of the clip stays the same.
Source footage
Raw unedited video that has been recorded by a camera.
Split screen
A method, created either in the camera or during the editing process, of telling two stories at the same time by dividing the screen into different parts. Unlike parallel editing, which cuts back and forth between shots for contrast, the split screen can tell multiple stories within the same frame.
Storyboard
A sequence of drawings representing the shots planned for a film or television production.
Sweetening
Post-production process of various filters and effects or otherwise enhancing the existing video. Basically, this means everything “extra”.
Time Code
A unique number based on hours, minutes, seconds, and frames that identifies each frame of video.
Timeline
Timeline is a commonly used interface found in most video editing programs. This interface enables authors to lay a video project out in a linear fashion horizontally across a monitor.
Track
Separate layers of video and audio used to record and edit sources individually.
Transition
A change from one shot to another.
Voiceover
A piece of narration in a movie or broadcast, not accompanied by an image of the speaker.
White Balance
A feature on digital cameras used to accurately balance color.
Wipe
A transition between shots in which a line passes across the screen, eliminating one shot as it goes and replacing it with the next one.